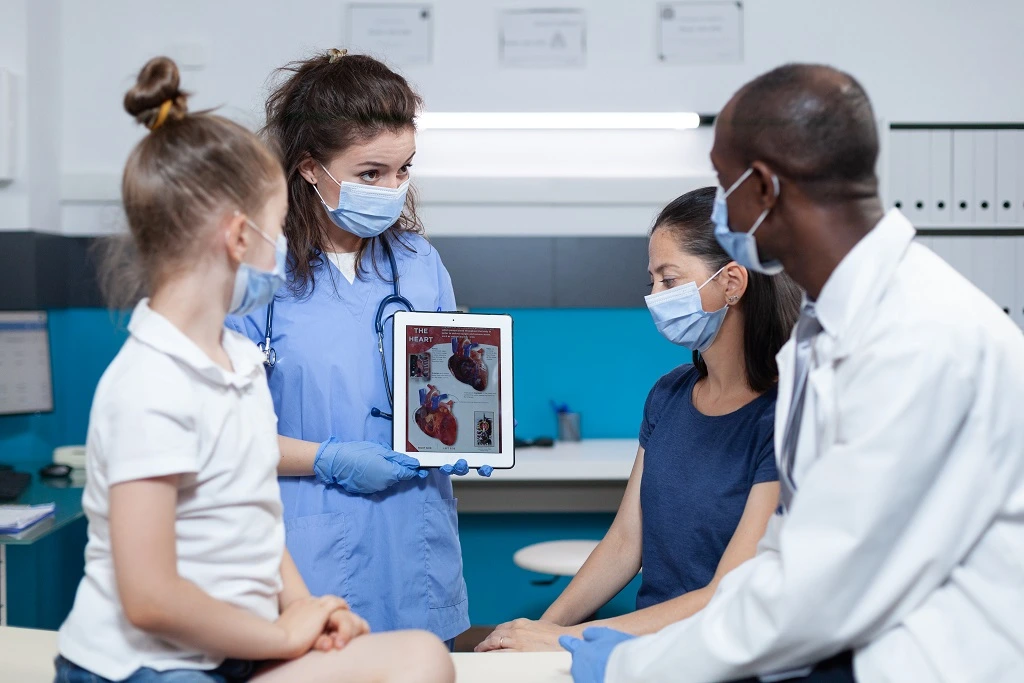
Patient care extends far beyond medical procedures and diagnoses, requiring healthcare professionals to also serve as effective educators. Whether you are a nurse, physician assistant, therapist, or medical assistant, the ability to explain conditions and treatments clearly is vital. Strong patient education skills not only improve understanding but also empower individuals to take control of their own health.
This blog will highlight why patient education are essential in healthcare careers and how they influence both patient outcomes and professional success. You will discover the core skills needed, practical examples from various roles, and strategies to strengthen these abilities. It will also provide guidance on showcasing patient education expertise effectively on your resume to stand out in the job market.
What Are Patient Education Skills?
Patient education skills refer to a healthcare professional’s ability to communicate medical information clearly, teach patients how to manage their conditions, and ensure they understand the steps required for recovery or ongoing care. It’s not just about relaying information; it’s about tailoring the message to each patient’s level of health literacy, cultural background, and emotional state.
At the core, these skills involve:
- Explaining diagnoses, medications, and procedures in simple terms.
- Encouraging patient engagement and questions.
- Using tools and resources to improve understanding (e.g., visual aids, digital tools, or demonstrations).
- Checking comprehension and reinforcing key points.
- Promoting adherence to treatment plans through motivational communication.
When done well, patient education fosters trust, improves health outcomes, and reduces hospital readmissions.
Why Patient Education Skills Matter in Healthcare
Every healthcare professional will encounter situations where clear communication and patient guidance are critical. For instance, a nurse explaining discharge instructions ensures patients don’t end up back in the emergency room. A physical therapist teaching proper exercises prevents re-injury. Even medical receptionists may need to explain insurance procedures or scheduling details in a way patients understand.
Here are the main reasons why patient education matter:
- Improved Patient Outcomes: Patients who understand their conditions and treatment plans are more likely to follow instructions and manage their health successfully.
- Enhanced Patient Satisfaction: Clear explanations and empathetic communication make patients feel valued and cared for, boosting satisfaction scores and trust.
- Reduced Healthcare Costs: By preventing readmissions and complications, effective patient education contributes to cost savings for both patients and healthcare institutions.
- Compliance with Regulations and Standards: Many healthcare organizations and accrediting bodies emphasize patient education as part of quality care metrics.
- Professional Advancement: Employers value staff who can balance clinical expertise with strong communication. Showcasing patient education skills on your resume highlights your ability to go beyond technical duties.
Core Patient Education Skills Every Healthcare Job Seeker Should Highlight
If you’re pursuing a career in healthcare, understanding which patient education skills to highlight is essential. Below are the most important ones:
1. Active Listening
Patient education starts with listening. Before providing information, healthcare professionals must understand the patient’s concerns, fears, and level of knowledge. Active listening shows empathy and ensures that the education provided is relevant.
2. Clear and Simplified Communication
Medical jargon can be intimidating. Breaking down complex terms into plain language is a valuable skill. For example, instead of saying “hypertension,” saying “high blood pressure” ensures better understanding.
3. Cultural Competence
Patients come from diverse backgrounds, and cultural beliefs often influence health behaviors. Healthcare workers must respect these differences and adapt their educational approach accordingly.
4. Teaching and Demonstration
Some instructions are better shown than explained. Demonstrating how to use an inhaler or showing proper wound care techniques can make a lasting impact on patient learning.
5. Use of Educational Tools
Visual aids, printed brochures, online resources, and videos enhance understanding. Knowledge of technology-based tools like patient portals or mobile health apps is becoming increasingly important.
6. Empathy and Compassion
Patient education is not just about facts—it’s about reassuring patients who may feel overwhelmed or scared. A compassionate approach helps patients absorb information better.
7. Assessment of Understanding
Checking patient comprehension through methods like “teach-back” (asking patients to explain instructions in their own words) ensures they truly grasp the information.
8. Motivational Skills
Patients may feel resistant to making lifestyle changes or adhering to treatment. Motivational interviewing helps encourage positive behavior change without judgment.
9. Adaptability
Not every patient learns the same way. Adjusting teaching methods—whether verbal, written, or hands-on—ensures that education is patient-centered.
10. Collaboration and Teamwork
Patient education is often a team effort. Nurses, physicians, pharmacists, and therapists may all contribute. Coordinating messages ensures consistency.
Practical Examples of Patient Education in Healthcare Roles
Different healthcare professionals integrate patient education in unique ways. Below are role-specific examples:
- Nurses: Teaching post-surgical patients wound care and medication schedules.
- Medical Assistants: Explaining vaccination procedures or lab preparation steps.
- Physician Assistants: Breaking down treatment options for chronic conditions like diabetes.
- Pharmacists: Counseling patients on safe medication use and potential side effects.
- Physical and Occupational Therapists: Guiding patients on at-home exercises for rehabilitation.
- Dietitians/Nutritionists: Providing meal plans and lifestyle advice for managing conditions like hypertension or obesity.
By tailoring patient education to their roles, healthcare workers can enhance the care experience and strengthen patient trust.
Building and Improving Patient Education Skills
If you’re preparing for a healthcare career, you may wonder how to improve your patient education skills. Here are some strategies:
- Pursue Professional Training: Many organizations offer workshops and certifications in health literacy and patient communication.
- Practice Role-Playing: Simulating patient interactions with peers or mentors builds confidence and adaptability.
- Leverage Technology: Familiarize yourself with patient portals, telehealth tools, and digital health apps to support education.
- Seek Feedback: Supervisors and colleagues can provide valuable insights into your communication style.
- Engage in Reflective Practice: After each patient encounter, reflect on what worked and what could be improved.
Showcasing Patient Education Skills on Your Resume
When applying for healthcare positions, don’t just list clinical skills—emphasize your patient education experience. Here are tips:
- Resume Summary: Mention your ability to deliver patient-centered care through clear communication and education.
- Skills Section: Add skills like health literacy awareness, active listening, motivational interviewing, and cultural competence.
- Work Experience: Provide examples, e.g., “Educated patients on chronic disease management, resulting in a 20% increase in treatment adherence.”
- Cover Letters: Share a story about how your patient education skills improved a patient’s outcome.
This demonstrates that you’re not only clinically capable but also a strong communicator—a highly desirable trait for employers.
The Future of Patient Education in Healthcare
As healthcare continues to evolve, patient education will remain a cornerstone of effective care. With the rise of digital health platforms, wearable technology, and remote monitoring, professionals will increasingly use technology-driven methods to engage and educate patients.
Moreover, as the focus shifts toward preventive care and chronic disease management, healthcare providers who excel in patient education will play an even more significant role in keeping populations healthy.
Enhance Your Resume with Patient Education Skills
Your ability to communicate and educate patients is just as important as your technical expertise. Make sure your resume highlights these vital patient education skills to stand out in a competitive job market. Our healthcare resume writing services are designed to showcase your strengths, from clinical expertise to communication excellence, ensuring hiring managers recognize your value.
Contact us today to get a resume that positions you as a top healthcare candidate who not only provides care but also empowers patients for better health outcomes.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Can patient education skills be measured during a job interview?
Yes. Employers often assess patient education skills through situational or behavioral interview questions. They might ask how you explained complex medical instructions to a patient or handled a situation where a patient didn’t initially understand your guidance.
2. Are patient education skills important for non-clinical healthcare roles?
Absolutely. Administrative staff, case managers, and medical receptionists often provide patients with information about processes, paperwork, or appointments. Their ability to explain clearly can reduce confusion and improve patient experiences.
3. What’s the biggest challenge in developing patient education skills?
One common challenge is addressing health literacy differences. Patients have varying levels of understanding, so healthcare professionals must adapt their approach without making patients feel overwhelmed or disrespected.
4. Do employers provide training for patient education skills, or should I learn them independently?
Many healthcare organizations offer in-house training or continuing education focused on communication and patient engagement. However, developing these skills independently—through workshops, online courses, or certifications—can make you more competitive.
5. How can I demonstrate patient education skills if I don’t have much work experience?
You can highlight experiences from clinical rotations, internships, or even volunteer work where you explained medical instructions, guided patients through processes, or helped individuals understand healthcare resources. Employers value potential and willingness to learn as much as experience.